The stability of global financial markets has become a critical concern for policymakers, economists, and investors alike. Uncertainty, often difficult to quantify, has emerged as a significant driver of financial market volatility. The ripple effects of economic uncertainty extend far beyond individual markets, influencing consumption, investment decisions, and credit availability.
Economic uncertainty encompasses a range of unpredictable factors that can affect the economy’s trajectory. Unlike traditional economic indicators, such as growth rates or inflation, which can be measured quantitatively, uncertainty is inherently more nebulous. Economists have developed various proxies to gauge uncertainty, one of the most recognized being the Economic Policy Uncertainty Index. This index analyzes how often major news publications reference uncertainty alongside economic and policy discussions.
Additionally, economists often assess the difference between actual economic data and prior forecasts to gauge uncertainty. When discrepancies arise between expected and actual economic performance, it highlights the challenges in predicting economic trends. With global economic conditions continually evolving, uncertainty has reached levels that can destabilize financial markets, delaying investment decisions and altering consumption patterns.
Despite a gradual recovery from the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, levels of economic uncertainty remain elevated. Factors such as surging inflation, geopolitical tensions, climate disasters, and rapidly evolving technologies contribute to this persistent uncertainty. The confluence of these elements highlights the importance of understanding how heightened uncertainty can undermine financial stability.
Factors Contributing to Heightened Uncertainty
Several key factors have exacerbated economic uncertainty in recent years. One of such is the pandemic’s aftermath. The COVID-19 pandemic fundamentally reshaped economies worldwide. As countries struggled to manage public health crises, the resulting lockdowns and supply chain disruptions led to unprecedented economic volatility. While many economies have started to recover, the lingering effects of the pandemic such as labor shortages and shifts in consumer behavior, continue to create uncertainty.
Moreover, inflationary pressures have also mounted. Inflation rates have surged in various economies, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, increased demand for goods, and rising energy prices. As central banks grapple with how to respond— whether to raise interest rates or implement other measures— uncertainty surrounding future inflation remains high.
Heightened geopolitical tensions, particularly in regions like Eastern Europe and East Asia, have further complicated the global economic landscape. Sanctions, trade wars, and military conflicts can disrupt markets and create an unpredictable economic environment, leading to increased volatility.
Climate-related events, including extreme weather and natural disasters, pose significant risks to economic stability. As countries work to adapt to climate change, the transition to greener economies can create uncertainty in traditional industries and financial markets.
Rapid technological advancements have also transformed industries but have also created uncertainty regarding the future of work, regulatory frameworks, and market dynamics. The rise of artificial intelligence, automation, and digital currencies have raised questions about job displacement and the stability of existing financial systems.
The Consequences of Heightened Uncertainty
The consequences of heightened uncertainty extend far beyond individual markets. Economic uncertainty can exacerbate financial turmoil. In times of heightened uncertainty, financial markets often react with increased volatility. Uncertain economic prospects can lead to sharp sell-offs in equities, increased bond yield spreads, and heightened currency fluctuations. As risk aversion rises, investors may seek safe-haven assets, exacerbating market turmoil.
Uncertainty can lead businesses and consumers to postpone investment and spending decisions. Companies may hold off on capital expenditures due to unclear economic conditions, while consumers may defer significant purchases amid concerns about job security and income stability. This reluctance to invest can hinder economic growth and prolong periods of stagnation.

Moreover, in an uncertain environment, lenders may tighten credit availability, making it more challenging for businesses and individuals to secure loans. This credit crunch can stifle economic activity and dampen consumer confidence, leading to a vicious cycle of reduced spending and investment.
Disconnect Between Economic Indicators and Market Behavior
An essential observation is that economic uncertainty does not always align with financial market behavior. The Global Financial Stability Report highlights instances where high economic uncertainty coexists with low financial market volatility.
Such disconnects can persist over time, creating a false sense of security in financial markets. However, when an unexpected shock occurs, market volatility can surge, leading to significant repercussions for the broader economy.
For example, if economic uncertainty were to escalate to levels seen during the global financial crisis, the downside tail risk, defined as the lowest decile of potential outcomes for economic growth, could drop by 1.2 percentage points. In practical terms, if the global economy is projected to grow by 0.5 percent in adverse conditions, this could shift to an expected contraction of 0.7 percent. Such shifts can have profound implications for employment, consumer spending, and overall economic stability.
The Macro-Financial Stability Tradeoff
The macro-financial stability tradeoff has to do with the balancing act that policymakers must navigate between maintaining financial stability and fostering economic growth. When financial conditions are loose, expectations for economic growth typically rise, and downside risks may appear reduced in the short term. Lower interest rates, higher asset valuations, and narrower credit spreads contribute to this dynamic.
However, easy financial conditions can also exacerbate debt vulnerabilities. Elevated levels of public and private debt can increase the likelihood of a financial crisis, particularly when economic uncertainty is high. For instance, during periods of economic expansion, easy credit conditions may encourage excessive borrowing, leading to unsustainable debt levels. In the face of an adverse shock, these vulnerabilities can surface, triggering a cascade of negative effects across the economy.
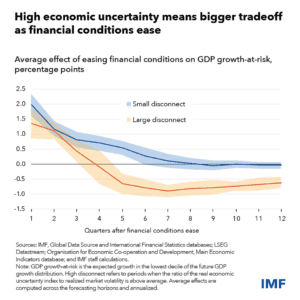
Meanwhile, the growing disconnect between economic fundamentals and financial market behavior is increasingly concerning. Financial markets may remain buoyant despite rising economic uncertainty, creating a sense of complacency among investors. However, such complacency can be precarious. If market conditions deteriorate suddenly due to an unforeseen shock, the consequences can be severe, leading to rapid declines in asset prices and increased credit constraints.
Moreover, this disconnect can create an environment where policymakers find it challenging to gauge the true health of the economy. Traditional economic indicators may not fully capture the risks lurking beneath the surface, making it crucial for policymakers to adopt a more comprehensive approach to monitoring economic conditions.
Safeguarding Financial Stability
Given the multifaceted challenges posed by economic uncertainty, it is imperative for policymakers to take proactive measures to safeguard financial stability. Several key strategies can help mitigate the risks associated with heightened uncertainty. One of the foremost responsibilities of policymakers is to enhance the credibility of their fiscal and monetary policy frameworks.
Establishing clear policy rules, supported by strong institutions, can help foster greater confidence among investors and consumers. When people perceive that policymakers are committed to sound economic management, they are more likely to make long-term investment decisions, reducing the negative impact of uncertainty.
Greater transparency and well-designed policy communication can better guide market expectations. Clear communication of policy decisions and their rationale can help mitigate uncertainty, allowing market participants to make more informed decisions. This predictability is particularly crucial in times of heightened economic uncertainty, as it can help stabilize markets and maintain investor confidence.
Policymakers should proactively implement macro-prudential policies to address the vulnerabilities associated with high levels of debt. These policies can include measures to limit excessive borrowing and reduce the likelihood of financial crises. For example, regulators may impose stricter lending standards or increase capital requirements for financial institutions to ensure they can withstand economic shocks.
Fiscal policies should prioritize sustainability to prevent elevated public debt levels from escalating borrowing costs. High borrowing costs can undermine macro-financial stability, as governments may struggle to finance essential services and investments. By adopting sound fiscal policies, governments can create a more stable economic environment, fostering growth and reducing volatility.
As heightened uncertainty can have cross-border spillover effects through trade and financial linkages, it is vital for policymakers to collaborate on international economic stability. Coordinated efforts can help mitigate the risks of international financial contagion– where economic shocks in one region can quickly spread to others.
As global financial stability remains under siege from a myriad of unknowns, understanding the relationship between economic uncertainty and financial market volatility is crucial. Policymakers must adopt a proactive approach, enhancing the credibility of their frameworks and utilizing macro-prudential policies to mitigate risks. The potential harms of economic uncertainty are significant, and recognizing their implications is essential for maintaining stability in the face of rising volatility.
The ongoing challenges posed by economic uncertainty necessitate a concerted effort from policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike. By prioritizing sustainable fiscal and monetary policies, enhancing transparency, and proactively addressing vulnerabilities, parties can work towards a more resilient global financial system. The stakes have never been higher, and the time for action is now.









