These technologies all have staying power. They will affect the economy and our politics, improve medicine, or influence our culture. Some are unfolding now; others will take a decade or more to develop. But you
can know about all of them from below:
 Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning
By experimenting, computers are figuring out how to do things that no programmer could teach them.
Reinforcement learning works because researchers figured out how to get a computer to calculate the value that should be assigned to, say, each right or wrong turn that a rat might make on its way out of its maze. Each value is stored in a large table, and the computer updates all these values as it learns. For large and complicated tasks, this becomes computationally impractical. In recent years, however, deep learning has proved an extremely efficient way to recognize patterns in data, whether the data refers to the turns in a maze, the positions on a Go board, or the pixels shown on screen during a computer game.
In fact, it was in games that DeepMind made its name. In 2013 it published details of a program capable of learning to play various Atari video games at a superhuman level, leading Google to acquire the company for more than $500 million in 2014. These and other feats have in turn inspired other researchers and companies to turn to reinforcement learning. A number of industrial-robot makers are testing the approach as a way to train their machines to perform new tasks without manual programming. And researchers at Google, also an Alphabet subsidiary, worked with DeepMind to use deep reinforcement learning to make its data centres more energy efficient. It is difficult to figure out how all the elements in a data centre will affect energy usage, but a reinforcement-learning algorithm can learn from collated data and experiment in simulation to suggest, say, how and when to operate the cooling systems. It is predicted to be available in 1 to 2 years.
 Reversing Paralysis
Reversing Paralysis
Scientists are making remarkable progress at using brain implants to restore the freedom of movement that spinal cord injuries take away. The French neuroscientist was watching a macaque monkey as it hunched aggressively at one end of a treadmill. His team had used a blade to slice halfway through the animal’s spinal cord, paralyzing its right leg. Now Courtine wanted to prove he could get the monkey walking again. To do it, he and colleagues had installed a recording device beneath its skull, touching its motor cortex, and sutured a pad of flexible electrodes around the animal’s spinal cord, below the injury. A wireless connection joined the two electronic devices. They were able to make the monkey walk again. These technologies could help thousands of people recover from paralyzing injuries each year. Projected availability is in 10 to 15 years.
 Self-Driving Trucks
Self-Driving Trucks
Tractor-trailers without a human at the wheel will soon inundate the highways near you. What will this mean for the global truck drivers? Continual developments are making long- haul trucks that drive themselves for extended stretches on highways more attainable. Significant challenges remain, including having sensors and code -match the situational awareness of a professional trucker. In the short term, this technology may welcome truck drivers to complete routes more efficiently, but it could also erode their pay and eventually replace many of them altogether. Key companies to watch in this area include Daimler, Otto, Peterbilt, and Volvo. Availability is prediction to be in five to 10 years.
 Paying with Your Face
Paying with Your Face
Face-detecting systems in China now authorize payments, provide access to facilities, and track down criminals. Will other countries follow? Using facial recognition technology to define the many unique features of a person’s face, algorithms are proving to be reliable enough to define identities through geometric and spatial calculations. Of the many applications for facial recognition, one of the potentially profitable is financial transactions. While these technologies are proving to be reliable, privacy concerns are being raised. Key companies in this area include Alibaba, Baidu, and Face++.
 Practical Quantum Computers
Practical Quantum Computers
Advances at Google, Intel, and several research groups indicate that computers with previously unimaginable power are finally within reach. This technology will revolutionize artificial intelligence and machine learning, specifically the area of constraint-based modelling. Solving complex simulations and scheduling problems inherent in complex supply chains and logistics systems is an area of research today. MIT Tech Review’s team also believes this technology could create uncrackable encryption. Key companies to watch in this area include Google, IBM, Intel, Microsoft, and QuTech. Projected availability is 4 to 5 years.
 The 360-Degree Selfie
The 360-Degree Selfie
Inexpensive cameras that make spherical images are opening a new era in photography and changing the way people share stories. We experience the world in 360 degrees, surrounded by sights and sounds. Until recently, there were two main options for shooting photos and video that captured that context: use a rig to position multiple cameras at different angles with overlapping fields of view or pay at least
$10,000 for a special camera. The production process was just as cumbersome and generally took multiple days to complete. Once you shot your footage, you had to transfer the images to a computer; wrestle with complex, pricey software to fuse them into a seamless picture; and then convert the file into a format that other people could view easily. Today, anyone can buy a decent 360° camera for less than $500, record a video within minutes, and upload it to Facebook or YouTube. Much of this amateur 360° content is blurry; some of it captures 360 degrees horizontally but not vertically; and most of it is mundane.
Producing 360° images and videos is predicted to be the new standard for news coverage and vacation shots and video. Several companies have cameras that will do this today. The leaders in this area include 360fly, Humaneyes Technologies, IC Real Tech, JK Imaging, Ricoh, and Samsung.
 Hot Solar Cells
Hot Solar Cells
By converting heat to focused beams of light, a new solar device could create cheap and continuous power. Standard silicon solar cells mainly capture the visual light from violet to red. That and other factors mean that they can never turn more than around 32% of the energy in sunlight into electricity. The MIT device is still a crude prototype, operating at just 6.8% efficiency—but with various enhancements it could be roughly twice as efficient as conventional photovoltaics.
The key step in creating the device was the development of something called an absorber- emitter. It essentially acts as a light funnel above the solar cells. The absorbing layer is built from solid black carbon nanotubes that capture all the energy in sunlight and convert most of it into heat. As temperatures reach around 1,000
°C, the adjacent emitting layer radiates that energy back out as light, now mostly narrowed to bands that the photovoltaic cells can absorb. The emitter is made from a photonic crystal, a structure that can be designed at the nanoscale to control which wavelengths of light flow through it. Another critical advance was the addition of a highly specialized optical filter that transmits the tailored light while reflecting nearly all the unusable photons back. This “photon recycling” produces more heat, which generates more of the light that the solar cell can absorb, improving the efficiency of the system. It shall be available from 10 to 15 years.
 Gene Therapy 2.0
Gene Therapy 2.0
Scientists have solved fundamental problems that were holding back cures for rare hereditary disorders. Next, we’ll see if the same approach can take on cancer, heart disease, and other common illnesses. Fixing rare diseases, impressive in its own right, could be just the start. Researchers are studying gene therapy in clinical trials for about 40 to 50 different diseases, says Maria-Grazia Roncarolo, a pediatrician and scientist at Stanford University who led early gene-therapy experiments in Italy that laid the foundation for Strimvelis. That’s up from just a few conditions 10 years ago. And in addition to treating disorders caused by malfunctions in single genes, researchers are looking to engineer these therapies for more common diseases, like Alzheimer’s, diabetes, heart failure, and cancer. Harvard geneticist George Church has said that someday, everyone may be able to take gene therapy to combat the effects of aging. Leading companies in this area include BioMarin, BlueBird Bio, GenSight Biologics, Spark Therapeutics, and UniQure.
 The Cell Atlas
The Cell Atlas
The centre of this innovation is the development of a master catalogue of every cell type in the human body. Having a precise taxonomy that can provide accurate models of human physiology will speed up the discovery and testing of new drugs. It’s predicted this will be available in 5 years. Behind the cell atlas are big- science powerhouses including Britain’s Sanger Institute, the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and a new “Biohub” in California funded by Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg. In September Zuckerberg and his wife, Priscilla Chan, made the cell atlas the inaugural target of a $3 billion donation to medical research.
 Botnets of Things
Botnets of Things
The relentless push to add connectivity to home gadgets is creating dangerous side effects that figure to get even worse. Botnets have existed for at least a decade. As early as 2000, hackers were breaking into computers over the Internet and controlling them en masse from centralized systems. Among other things, the hackers used the combined computing power of these botnets to launch distributed denial-of-service attacks, which flood websites with traffic to take them down.
But now the problem is getting worse, thanks to a flood of cheap webcams, digital video recorders, and other gadgets in the “Internet of things.” Because these devices typically have little or no security, hackers can take them over with little effort. And that makes it easier than ever to build huge botnets that take down much more than one site at a time. Botnets pose a security risk to large-scale areas of the Internet today. Predicated on the Mirai botnet software, this innovation underscores how essential security is for any Internet of Things device, system or platform.
THE CONCEPTS: CARS OF THE FUTURE

Cars are becoming more computer-like every day. We’re not just talking about advancements in self-driving tech, either. Automakers know that cars today have to be smart and easy to use. One of the most exciting things to an automotive enthusiast is taking a look at the innovative future technology of the industry. Every year, automakers try to go above and beyond what they (and their competitors) have done before in terms of functionality, safety, and performance. While the industry isn’t quite as quick to fully adopt new tech like phones, computers and other electronics, it seems that with every passing year even the newest vehicles can feel instantly out-dated. A lot of these innovations can still only be seen in concept cars, but they offer a glimpse of how companies are working to radically change the car of the future. Below are some concept cars for the future.
 Faraday Future FF91- The 1,050bhp electric car that accelerates faster than a Ferrari
Faraday Future FF91- The 1,050bhp electric car that accelerates faster than a Ferrari
When it comes to the electric car market there is no name more well-known than Tesla. From the original roadster to their complete line- up with a sedan, crossover and soon-to-be daily electric car for the masses, they have the market cornered. But with all that attention comes plenty of new-comers eager to take the crown. The latest, and potentially most viable competitor, is the Chinese-backed, Silicon Valley start-up Faraday Future.
Faraday’s new FF91 can accelerate faster than any other electric car in production including the Tesla Model S. The new electric car was revealed at CES 2017 in Las Vegas and is the first production car to be announced by the start-up. Faraday’s first car has however been met with scepticism since they first appeared at the Las Vegas show last year. Faraday asserts the car can achieve 378 miles of range one single charge and added that its range would extend to 482 miles (775km) when driven at 55mph. The car company also teased super-fast charging for the car. Faraday’s FF91 looks like a sporty SUV combining elements of both the Tesla Model X and BMW i8 in terms of style, but also featuring these futuristic curved grilles on both the front and back of the car. The FF-ID is an interesting and unique feature.
It offers a personalised driving experience to the driver including the position of the front seat, applications you use, and music you listen to. It is not the best looking car in the work but it looks trendy, sporty and modern. Faraday Future’s FF91 will go from 0-62mph in just 2.39 seconds. This makes it one of the fastest accelerating cars in the world.
People interested in the FF91 can declare their interest and place a refundable $5000 deposit online and create own FFID.
 Lexus’ concept SUV, the UX, gives us a sneak peek of how cars will one day drive around without any mirrors.
Lexus’ concept SUV, the UX, gives us a sneak peek of how cars will one day drive around without any mirrors.
Unveiled at the Paris Motor Show, the UX has cameras instead of side view mirrors. This isn’t the first time we’ve seen a concept car without mirrors, but it’s worth paying some extra attention to the feature showing up on a Lexus. Japanese automakers got the OK in June 2016 to make and sell mirrorless cars, making it one of the first countries to embrace the technology. Considering Lexus is owned by Japanese automaker Toyota, we’re likely to see more of this tech in use going forward.

Honda NeuV – The car that THINKS
HONDA releases a future concept car, with Artificial Intelligence, an electric skateboard and also that can earn money.
AI is becoming a bit of a buzzword in our technological world today. Car manufacturers are stating their interest in autonomous cars, and next -generation tech, to support the experience of driving (or not driving). Honda has however taken this to the next level, creating a car that will transform the way we interact with cars in the future. Inside, Hana the AI, pays attention to the driver’s likes and dislikes and can ever remember tour favourite places such as coffee shops. Hana can check on the driver’s emotional well-being, make music recommendations based on mood, and support the owner’s daily driving routine. Hana uses a heart-rate monitor and face recognition to detect when you’re stressed and can suggest that you take a break, suggesting one of your favourite spots to stop at. The car uses technology called Safe Swarm which allows the car to communicate with other cars around it, enabling more efficiency, less stressful and more importantly collision-free driving.
In addition to this, Hana can work for you. While it is parked outside your home or office, it can nip-off and act as a ride-sharing service, which can drive people around to earn you money. Alternatively, it can sell back power to the grid at a peak time, and charge them to replenish it at an off peak time, which again can make you money. The doors are pretty spectacular, comprising the whole side panel of the car, spinning up electronically at the touch of a button. This should aid practicality, helping you squeeze into the compact city-car when there is not much room. Inside the car there is also an electric skateboard designed as a ‘last mile’ solution, to help you escape gridlock traffic and get to work on time.
 Mercedes-Benz Concept EQ SUV
Mercedes-Benz Concept EQ SUV
Mercedes’s Concept EQ SUV and the Vision Van debuts stay in line with its new corporate strategy called “CASE,” or Connected, Autonomous, Shared & Service, and Electric Drive. Working on pure battery electric drive systems, the tech found on the Concept EQ, a rival to the Tesla Model X, is expected to be carried into the future Mercedes cars. The Vision Van, meanwhile, is a study for the delivery van of the future, combining an electric powertrain and a trick integrated system for more efficient deliveries.
 Toyota Concept-i: The AI car that builds ‘relationships’ with humans
Toyota Concept-i: The AI car that builds ‘relationships’ with humans
Toyota has unveiled the futuristic driverless Concept-i, which is said to be built around the driver’s needs and fitted with the latest AI technology. The new concept car uses an advanced artificial intelligence system to anticipate the driver and passenger’s needs and Toyota says it can ‘spur their imaginations and improve their lives.’
The Japanese car manufacturer’s AI system learns with the driver, building a relationship and improves as the vehicle is driven. In addition to this, the AI system automated vehicle technologies is designed to help improve safety, using visual and touch prompts to augment communication based on the driver’s responsiveness. Toyota has designed the car from the inside-out starting with the next generation user interface that provides the platform for the vehicle’s AI agent, nicknamed ‘Yui.’ The Japanese car firm has said Yui has been designed to ‘connect with a global audience.’ Yui can use light, sound and even touch to communicate crucial information to the driver. Even the vehicle’s exterior is designed to enable Concept-i to engage with the world around it. Yui appears on the door panels to welcome driver and passengers as they approach the vehicle. The rear of the car displays messages about upcoming turns or warnings of potential hazards, while the front communicates whether automated or manual drive is engaged.
 Mercedes Vision Van debuts– futuristic van comes with DRONES and ROBOTS
Mercedes Vision Van debuts– futuristic van comes with DRONES and ROBOTS
This bizarre-looking electric van is designed to work with a drone to optimize package delivery. Mercedes’ Vision Van is part of a $562 million investment over the next five years to create a network of all-electric vans and drones for a rapid delivery service. The van has a fully automated cargo space that loads packages and alerts the driver when approaching a drop-off location for one of them. It will then push that package through a hatch on the roof so a drone can grab it and fly it to the right location. It’s still unclear when we’ll see the van in use, but it’s an interesting step showing Mercedes’ intent to revolutionize the logistics of package delivery.
 BMW Vision Next 100 concept
BMW Vision Next 100 concept
This concept car is loaded with innovative features, but the one we can’t stop talking about is its wheels.
The wheels on the BMW Vision Next 100 concept are essentially one with the car, allowing them to make this beautifully sleek movement when the steering wheel is turned. It’s a really tiny detail, but it shows a new interest in rethinking the general design or aesthetic of a car. We just hope changing a flat tire isn’t too cumbersome if this ever comes to fruition.


 Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning Reversing Paralysis
Reversing Paralysis Self-Driving Trucks
Self-Driving Trucks Paying with Your Face
Paying with Your Face Practical Quantum Computers
Practical Quantum Computers The 360-Degree Selfie
The 360-Degree Selfie
 Hot Solar Cells
Hot Solar Cells Gene Therapy 2.0
Gene Therapy 2.0 The Cell Atlas
The Cell Atlas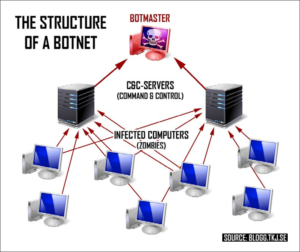 Botnets of Things
Botnets of Things Faraday Future FF91- The 1,050bhp electric car that accelerates faster than a Ferrari
Faraday Future FF91- The 1,050bhp electric car that accelerates faster than a Ferrari Lexus’ concept SUV, the UX, gives us a sneak peek of how cars will one day drive around without any mirrors.
Lexus’ concept SUV, the UX, gives us a sneak peek of how cars will one day drive around without any mirrors. Mercedes-Benz Concept EQ SUV
Mercedes-Benz Concept EQ SUV Toyota Concept-i: The AI car that builds ‘relationships’ with humans
Toyota Concept-i: The AI car that builds ‘relationships’ with humans Mercedes Vision Van debuts– futuristic van comes with DRONES and ROBOTS
Mercedes Vision Van debuts– futuristic van comes with DRONES and ROBOTS BMW Vision Next 100 concept
BMW Vision Next 100 concept





